Long term care insurance applications must contain plain and unambiguous – Long-term care insurance applications must contain plain and unambiguous language to ensure clear communication between the applicant and the insurer. This is crucial for avoiding misunderstandings and potential legal issues. Imagine trying to navigate a complex maze without clear directions; that’s akin to navigating a long-term care application with confusing language. This guide delves into the importance of straightforward language, exploring how to craft applications that are not only easily understood but also legally sound.
The focus is on simplifying the application process. By using clear and precise language, prospective clients can feel confident in their choices, and insurers can avoid disputes down the line. This guide provides a practical approach to crafting applications that are both accessible and legally sound. We’ll also discuss how these principles promote accessibility for diverse demographics and ensure inclusivity.
Clarity and Precision in Application Language
Clear and unambiguous language is paramount in long-term care insurance applications. Precise wording prevents misunderstandings, ensuring accurate assessment of risk and proper policy issuance. This approach safeguards both the applicant and the insurance provider, fostering trust and avoiding potential legal disputes down the line.
Importance of Plain Language
Using plain and unambiguous language in long-term care insurance applications is crucial for several reasons. It ensures that applicants fully comprehend the terms and conditions of the policy. This clarity minimizes the risk of misinterpretations, leading to fairer and more equitable outcomes for all parties involved. Ambiguous language can inadvertently create loopholes or uncertainties, potentially impacting the financial security and peace of mind of the policyholder.
Examples of Unclear Language
Vague or overly technical language can obscure the true meaning of application provisions. For example, a clause stating “potential future needs” without specific details on the types of care covered could lead to disputes if a claim is denied. Similarly, a question about “pre-existing conditions” without a clear definition of what constitutes a pre-existing condition might result in the applicant inadvertently omitting critical information, potentially affecting the insurance coverage.
These instances highlight the need for meticulous phrasing and comprehensive explanations.
Legal Ramifications of Ambiguous Language
Ambiguous language in insurance contracts can have significant legal ramifications. Courts may interpret such language in favor of the policyholder, potentially leading to payouts even if the insured’s situation falls outside the intended scope of the policy. Conversely, ambiguous language could allow the insurance company to deny claims, even if the policyholder’s situation clearly aligns with the policy’s terms.
Precise language reduces the risk of costly and time-consuming legal battles.
Ensuring Clarity in Terms and Conditions
To guarantee clarity in terms and conditions, several steps must be taken. First, consult with legal professionals to ensure all provisions are legally sound and appropriately phrased. Second, use clear and concise language that avoids jargon or technical terms. Third, provide examples illustrating the policy’s application in various scenarios. Finally, review the application with potential applicants, providing ample opportunity for questions and clarifications.
Clear vs. Ambiguous Phrasing
| Section of Application | Clear Phrasing | Ambiguous Phrasing |
|---|---|---|
| Eligibility Criteria | “Applicants must be at least 65 years of age and have resided in the state for at least five years.” | “Applicants must meet age and residency requirements.” |
| Covered Services | “The policy covers skilled nursing care, home health aide services, and assisted living facilities.” | “The policy covers various types of long-term care services.” |
| Exclusions | “The policy does not cover pre-existing conditions diagnosed within the last 12 months.” | “The policy excludes certain pre-existing conditions.” |
| Claim Process | “To file a claim, submit a completed claim form, supporting documentation, and a physician’s statement.” | “Claims must be submitted according to company procedures.” |
Defining “Plain and Unambiguous”
Plain and unambiguous language in insurance applications is crucial for clarity and comprehension. This ensures that policyholders understand their rights and responsibilities without ambiguity, reducing potential misunderstandings and disputes. A clear and concise approach helps avoid confusion and promotes informed decision-making.Defining “plain and unambiguous” in insurance applications requires a multifaceted approach. It transcends simple readability, delving into the specific nuances of insurance jargon and the importance of clear, straightforward explanations.
This includes avoiding technical terms and using everyday language, as well as presenting information in a logical and structured manner.
Defining Plain and Unambiguous Language
Plain and unambiguous language in insurance applications avoids complex sentence structures and specialized vocabulary. It uses everyday words and phrases, ensuring the information is accessible to a broad audience. This approach is essential for effective communication and minimizes the potential for misinterpretation.
Avoiding Jargon and Technical Terms
Using jargon or technical terms can significantly hinder comprehension. Insurance applications often include terms like “rescission,” “indemnification,” and “subrogation,” which may not be familiar to all readers. Replacing these terms with simpler alternatives improves accessibility and promotes a more user-friendly experience.
Examples of Problematic Terminology
- Instead of “Contingency Reserves,” use “Emergency Funds.”
- Instead of “Actuarial Assessment,” use “Risk Evaluation.”
- Instead of “Subrogation,” use “Claim Recovery.”
These examples illustrate the importance of replacing complex terms with simpler, more easily understood alternatives.
Potential Pitfalls of Using Jargon
Using jargon can lead to misunderstandings and misinterpretations. Technical terms, even if understood by insurance professionals, may not be clear to the average policyholder. This can result in confusion about coverage, benefits, or responsibilities, potentially leading to disputes.
Different Styles for Clarity
Different writing styles can significantly impact clarity. A concise, direct approach using active voice and short sentences is often more effective than complex sentence structures and passive voice. Employing headings, bullet points, and clear visual aids can further enhance understanding.
Comparison of Clear and Unclear Writing Styles
- Clear Style: “The policy covers accidental injuries sustained while traveling.”
- Unclear Style: “Coverage is afforded for fortuitous harm sustained while en route.”
The clear style directly conveys the meaning using familiar terms. The unclear style uses more technical language that may be less easily understood by the average reader.
List of Common Legal Terms and Simpler Alternatives, Long term care insurance applications must contain plain and unambiguous
| Legal Term | Simpler Alternative |
|---|---|
| Rescission | Cancellation |
| Indemnification | Compensation |
| Subrogation | Claim Recovery |
| Beneficiary | Recipient |
| Insured | Policyholder |
| Coverage | Protection |
Impact on Customer Understanding
Clear and concise language in long-term care insurance applications significantly improves customer comprehension and reduces confusion. This translates directly to higher customer satisfaction and a more effective application process. Understanding the policy terms and conditions becomes paramount for informed decision-making.Well-structured applications, free from jargon and complex phrasing, empower prospective clients to grasp the nuances of the policy and its implications.
This fosters trust and encourages a more positive perception of the insurance product and the provider.
Improved Policy Comprehension
Clear language in long-term care insurance applications directly impacts how easily customers understand the policy’s terms and conditions. By eliminating ambiguity and using straightforward language, customers can more readily grasp the coverage, exclusions, and limitations of the policy. This understanding is essential for informed decision-making.
Reduced Customer Confusion
Jargon and complex legal terminology are common obstacles in insurance applications. Replacing these with simple, everyday language dramatically reduces customer confusion. This simplification allows prospective clients to focus on the essential aspects of the policy, leading to a more informed decision-making process.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
A straightforward application process, supported by clear communication, leads to increased customer satisfaction. Customers who feel understood and empowered by the application process are more likely to feel positive about the insurance product and the provider. This positive perception is a crucial element in fostering long-term relationships.
Benefits of a Clear Application Process
A well-designed application process, emphasizing clear communication, offers numerous benefits for prospective clients. This includes fostering trust, enabling informed decisions, and increasing the likelihood of a positive customer experience.
Creating Applications Focused on Customer Understanding
| Step | Description | Focus on Customer Understanding |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Policy Summary | Provide a concise and easily understandable overview of the policy’s key features. | Clearly Artikel the coverage, exclusions, and benefits in simple language, avoiding technical jargon. Include specific examples of situations covered or excluded. |
| 2. Glossary of Terms | Include a glossary defining all technical terms or insurance-specific language. | Ensure definitions are clear and accessible, using everyday language. Provide examples illustrating the use of each term within the context of the policy. |
| 3. Benefit Illustrations | Use visual aids (charts, graphs, or examples) to illustrate policy benefits and how they apply in various scenarios. | Illustrate the potential financial outcomes under different circumstances, showing the benefits in a practical and relatable manner. |
| 4. Simplified Explanations | Provide plain-language explanations of complex concepts. | Avoid technical jargon and complex legal phrasing. Use simple analogies or real-world examples to illustrate the concept. |
| 5. Customer Feedback Mechanisms | Include mechanisms for gathering feedback on the clarity and understandability of the application. | Actively solicit feedback from prospective clients to identify areas for improvement in the application’s language and structure. |
Accessibility and Inclusivity
Plain language in long-term care insurance applications significantly enhances accessibility for diverse customer demographics. By employing clear, concise language, providers can remove barriers to understanding for individuals with varying literacy levels, disabilities, or limited English proficiency. This fosters trust and empowers consumers to make informed decisions about their financial future.Improving accessibility through plain language is not just a matter of compliance; it’s a critical component of ethical and responsible business practices.
Long-term care insurance applications, folks, need crystal-clear language. No room for ambiguity! Want to know if something else is covered by insurance? Figuring out if is nipt testing covered by insurance can be tricky too, but clear application language is key for everyone, from long-term care to practically anything else. So, keep those applications simple and straightforward!
By actively considering the diverse needs of potential customers, companies can build a more inclusive and equitable marketplace. This commitment translates to a wider reach and improved customer satisfaction, ultimately benefiting both the insurer and the insured.
Tailoring Language for Different Literacy Levels
Understanding that individuals have varying degrees of literacy is crucial for creating accessible applications. A single, standardized approach will not meet the needs of all potential customers. Strategies for tailoring language include:
- Using shorter sentences and paragraphs.
- Employing everyday words and avoiding jargon.
- Breaking down complex concepts into simpler steps or examples.
- Providing visual aids like charts or diagrams to clarify information.
- Offering multiple formats (e.g., print, audio, large print).
For example, instead of “Actuarial projections indicate a likely premium increase,” use “Our estimates show premiums may go up.” Such modifications make the information easier to comprehend and apply.
Long-term care insurance applications need crystal-clear language, no room for confusion. Knowing how to interpret policy wording is crucial, which is why studying for your P&C insurance exam prep can be a big help. p&c insurance exam prep will sharpen your ability to spot ambiguities in contracts, which directly translates to better understanding of those crucial long-term care applications.
After all, clear applications lead to smoother claims processes, which is the name of the game.
Employing Inclusive Language
Inclusive language avoids potentially biased or exclusionary terms. This extends beyond simple word choices to consider the broader context and cultural nuances.
- Avoid gendered pronouns where possible (e.g., use “individuals” instead of “he/she”).
- Use culturally neutral language that doesn’t assume a particular background or experience.
- Acknowledge and respect different abilities and disabilities.
- Avoid terms that may be considered discriminatory or stigmatizing.
For instance, replacing “active duty military” with “military personnel” can reflect a more comprehensive and respectful approach.
Sample Application Form
| Question | Plain Language Version |
|---|---|
| What is your current employment status? | Are you currently working, retired, or not working? |
| Describe any pre-existing medical conditions. | Please tell us about any health problems you have had or are currently experiencing. |
| What is your desired coverage amount? | How much coverage do you need for your long-term care? |
| Please list any dependents. | Who else do you want to be included in this plan? |
| Do you have any questions about this form? | Is there anything you don’t understand or need clarification on? |
This table demonstrates how simple, direct language can significantly improve understanding while maintaining the necessary information.
Structuring the Application for Clarity
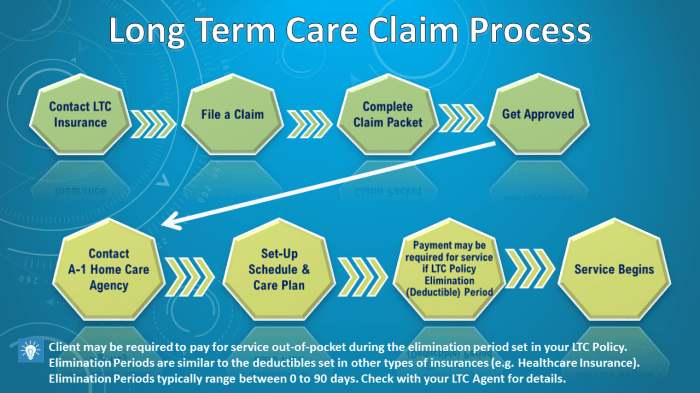
A well-structured long-term care insurance application is crucial for ease of comprehension and accurate completion. Clear organization facilitates understanding of the application’s requirements and minimizes errors. This section details methods for presenting information logically and sequentially, using headings, subheadings, and bullet points effectively, and incorporating visuals for enhanced clarity.Effective structuring streamlines the application process, reducing customer burden and increasing the likelihood of accurate responses.
It directly impacts customer understanding and reduces the potential for misinterpretation, thereby improving the overall application experience.
Logical Section Arrangement
The application should be divided into logical sections, each focusing on a specific aspect of the coverage. This approach allows applicants to concentrate on one area at a time, reducing cognitive load and improving comprehension. For example, a section dedicated to applicant details should be followed by a section on coverage options, and then by a section on premiums and payment methods.
This progression ensures a seamless and manageable flow.
Using Headings and Subheadings
Employing clear and concise headings and subheadings is essential. They act as signposts, guiding the applicant through the application process. These headings should clearly reflect the content of the subsequent section, making the application intuitive and easy to navigate. For example, “Personal Information” could be a main heading, with subheadings like “Contact Details,” “Date of Birth,” and “Address History.”
Bullet Points for Key Information
Use bullet points to present key information concisely and efficiently. This method highlights important details and makes the application more visually appealing. For instance, when describing coverage options, use bullet points to list the different types of care included, the geographical coverage areas, and the exclusions.
Visual Aids for Enhanced Clarity
Incorporating visuals, such as charts or diagrams, can significantly improve understanding, particularly when dealing with complex information. A chart illustrating the different coverage levels and associated premiums, or a diagram outlining the claims process, can greatly assist the applicant. For instance, a table comparing policy options side-by-side can aid in the decision-making process.
Example Section Arrangement Table
| Section | Content | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Applicant Information | Name, address, date of birth, contact details | Establishes the applicant’s identity and location. |
| Coverage Options | Different types of care, coverage periods, geographical areas | Highlights the available options and their scope. |
| Financial Information | Income details, assets, payment history | Evaluates the applicant’s financial capacity to meet premiums. |
| Medical History | Past medical conditions, medications, hospitalizations | Assesses the applicant’s health risks and determines premium rates. |
| Beneficiary Information | Details of the individuals who will receive benefits | Identifies individuals who will be entitled to the policy benefits in case of claim. |
Examples of Clear Language in Action
Clear and concise language is crucial for long-term care insurance applications. Using simple, everyday terms and avoiding jargon ensures that policyholders understand their coverage, benefits, and exclusions without confusion. This approach fosters trust and facilitates informed decision-making.This section demonstrates how clear language can be implemented across various application components, from policy descriptions to frequently asked questions. It emphasizes the importance of straightforward sentence structures and precise wording to convey complex information effectively.
Coverage Descriptions
Clear definitions of coverage are essential for understanding what is included and what is excluded. Instead of using complex legal jargon, use plain language to describe the benefits.
- Instead of: “The policy provides comprehensive coverage for the cost of care services within the specified limitations.”
- Use: “This policy pays for skilled nursing care, assisted living, and home healthcare.”
- Instead of: “Eligible expenses are subject to a maximum benefit amount determined by the benefit schedule as per policy terms.”
- Use: “The maximum amount we pay for your care is $X per month.”
Exclusions
Clearly outlining exclusions is equally vital. This transparency prevents misunderstandings and ensures that policyholders are aware of what the policy does
not* cover.
- Instead of: “Certain pre-existing conditions may not be covered as per the policy terms.”
- Use: “We don’t cover care for conditions you had before purchasing this policy.”
- Instead of: “The policy excludes coverage for care in a facility not recognized by the insurer.”
- Use: “We won’t pay for care at facilities we don’t approve.”
Simple Sentence Structures for Complex Information
Using simple sentence structures can effectively convey complex information. Break down long, convoluted sentences into smaller, easier-to-understand parts.
- Instead of: “Due to the complexity of the various eligibility requirements, it is crucial to carefully review the policy terms and conditions to understand the specific criteria that must be met.”
- Use: “To qualify, you need to meet specific requirements. Review the policy details for specifics.”
- Instead of: “The insured must be enrolled in the program for a minimum of three years for eligibility to apply for a coverage increase.”
- Use: “To qualify for a coverage increase, you must be enrolled for at least three years.”
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Clear and concise FAQs address common questions about the policy, promoting transparency and minimizing confusion. Use simple language and avoid technical terms.
- Instead of: “The application process involves several stages of verification, as per the guidelines established in the policy documents.”
- Use: “Our application process has several steps. We need certain documents to process your request.”
- Instead of: “The waiting period for coverage varies based on the type of care.”
- Use: “The waiting period for coverage depends on the type of care. Check the policy for specifics.”
Comprehensive Application Example
This document Artikels a comprehensive long-term care insurance application example, emphasizing clarity and precision in language. It showcases the application’s structure, including coverage details, exclusions, and FAQs, using simple, direct language. The document ensures easy comprehension and minimizes ambiguity.
Evaluating Application Clarity: Long Term Care Insurance Applications Must Contain Plain And Unambiguous
Ensuring long-term care insurance applications are easily understood by potential customers is crucial for accurate and informed decision-making. A robust evaluation process is vital to identify and address any ambiguity or complexity in the language used. This process should focus on both the form’s structure and the clarity of the individual questions and explanations.A well-designed evaluation process should be able to identify potential problems with the application before it’s finalized, saving time and resources in the long run, while reducing the likelihood of misunderstandings or errors on the part of the applicant.
Process for Evaluating Application Clarity
A systematic process is essential to ensure the application is clear and understandable. This involves multiple stages and perspectives. Begin with a comprehensive review of the language employed in the application.
- Initial Review by Subject Matter Experts: Insurance professionals and legal experts with knowledge of long-term care insurance policies should thoroughly examine the application form. They should assess the terminology, phrasing, and overall clarity of each question and section. This ensures technical accuracy and adherence to legal requirements.
- Review by Potential Customers: Gather a representative sample of potential customers, similar in demographics and financial background to the target market. Present them with the application and observe their responses and identify areas of confusion or difficulty. Qualitative data collection methods, like focus groups and individual interviews, can help uncover hidden problems with comprehension.
- Focus Group Discussions: These discussions allow for in-depth exploration of how individuals understand different sections of the application. By observing reactions and asking clarifying questions, insights into potential areas of difficulty can be gained. Open-ended questions are critical to elicit honest feedback.
- Cognitive Walkthrough: Experts should step through the application as if they were a typical customer. They should identify any points where they might get stuck or confused, noting the specific language or formatting issues that contribute to the difficulty. This is a critical step to improve the application’s ease of use.
Methods for Assessing Plain and Unambiguous Language
The language employed in the application must be simple, precise, and avoid jargon. A key method for evaluation is to conduct readability tests.
- Readability Formulas: Utilize readability formulas (like the Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level) to objectively assess the complexity of the language. This helps ensure the application is accessible to a wide range of individuals.
- Dictionary Review: Verify that all terms used are clearly defined and have common, easily understood meanings. Check for any potential ambiguity in terminology or technical language. This should include verifying if the terminology aligns with commonly accepted definitions within the insurance industry.
- Plain Language Guidelines: Apply plain language guidelines to the entire application, ensuring that the language is straightforward, concise, and avoids overly complex sentence structures. Examples of simple and clear language will help guide the process.
Metrics for Measuring Customer Understanding
Quantifiable metrics are important for assessing the impact of clarity improvements.
| Metric | Description | Measurement |
|---|---|---|
| Completion Rate | Percentage of potential customers who successfully complete the application form. | Calculate the percentage of individuals who complete the application form compared to those who started it. |
| Number of Clarifying Questions | The number of clarifying questions asked by potential customers during the application process. | Track the number of questions asked by individuals seeking clarification or further explanation. |
| Customer Feedback Surveys | Assess the level of understanding of the application through post-application surveys. | Utilize surveys to gauge customer comprehension, using questions about understanding of specific sections or overall process. |
Methods to Review Application Forms for Comprehension
A multi-faceted approach to reviewing the application form is necessary.
- Expert Review: Legal and insurance professionals should review the form for clarity, accuracy, and compliance with industry standards. This review should focus on technical accuracy and adherence to relevant regulations.
- Simulated Application: Allow individuals to complete the application under simulated conditions to identify any areas where assistance or clarification is needed. This method helps gauge comprehension in a realistic setting.
- Pilot Testing: A pilot test allows for a small-scale assessment of the application with a representative sample. This provides real-world data on application clarity and helps to pinpoint specific areas for improvement.
Checklist for Reviewing Application Form Clarity
A checklist provides a structured approach to evaluating application clarity.
| Criteria | Evaluation |
|---|---|
| Simplicity of Language | Is the language clear, concise, and easily understood by a wide range of individuals? |
| Unambiguous Terms | Are all terms and concepts defined and used consistently? |
| Readability | Does the application meet readability standards for the target audience? |
| Completeness | Are all necessary details and information included? |
| Logical Flow | Is the application structured in a logical order that facilitates understanding? |
| Accessibility | Is the application accessible to individuals with disabilities? |
Final Review
In conclusion, crafting clear and unambiguous long-term care insurance applications is not just good practice; it’s essential. By prioritizing plain language, insurers can build trust with potential clients and foster a smooth application process. The guide provided demonstrates how clarity, accessibility, and legal soundness go hand in hand in ensuring a positive experience for all involved. By applying the principles Artikeld here, the application process becomes less daunting and more trustworthy.
Expert Answers
What are some common pitfalls to avoid when writing long-term care applications?
Using jargon, overly complex sentence structures, and ambiguous terms can lead to misunderstandings. Instead, use simple, straightforward language, avoiding legalistic terms where possible. Define all terms that might be unclear to the average reader.
How can I ensure my application is accessible to all potential clients?
Use inclusive language, avoiding biased or exclusionary terms. Consider the different literacy levels of your potential clients and tailor your language accordingly. Provide clear visual aids and alternative formats for those with specific needs.
What is the importance of legal compliance when writing long-term care applications?
Clarity and precision are essential to avoid legal issues. Using unambiguous language ensures that both parties understand the terms and conditions, minimizing the risk of disputes and misunderstandings.
How can I structure my application form for maximum comprehension?
Organize the form logically, using clear headings, subheadings, and bullet points. Use visuals to complement the text and enhance understanding. Consider the overall flow and presentation to make it easy to navigate.
